What is MMC (Microsoft Management Console) and what are MMC snapin files
Windows Client and Server Operating Systems are included with an app called Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Microsoft Management Console (MMC) app is used mainly to perform administrative tasks in Windows Operating Systems. Tasks related with managing and maintaining the hardware and software of a Windows based Server can be performed using Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Custom tools to manage and maintain your Operating Systems can be created by using MMC.
What are MMC snap–in files
There are many files called snap–ins included with Windows Server 2025. These snap–in files can be opened using MMC. Each snap–in has different functionality for performing different tasks ralated with the management and maintenance of your Server Operating System.
Most of the in–built snap–in files in Windows Server 2025 are located inside %systemroot%/System32 folder. Please note that the %systemroot% system variable contains the path to your Windows Server installation folder, for example C:\Windows. If you want to know your Windows installation folder, type echo "%systemroot%" inside your Command Prompt terminal and press "Enter" key.
Please refer below command to find your Windows installation folder. In this example, it is C:\WINDOWS folder.
C:\jajish>echo %systemroot% C:\WINDOWS
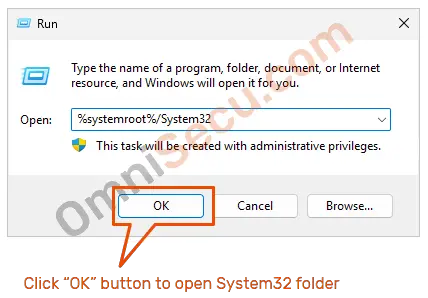
If you want to open your %systemroot%/System32 folder, type %systemroot%/System32 in your Windows Run box, and then click "OK" button. If you are not sure how to open Windows Run dialog box, press Windows and R keys together.
Warning 
Most of the files stored in Windows installation folder are Windows Operating System related system files. Do not try to delete or modify any file in your Windows installation folder. You can completely damage your Windows Server Operating System by deleting or modifying a file in your Windows installation folder.
Some important MMC snap–in files
An MMC snap–in file has .msc file extension. Following are some important MMC snap–in files stored in %systemroot%/System32 folder.
| MMC snap–in File name | Name of the snap–in | Short description |
|---|---|---|
| azman.msc | Authorization Manager | Authorization Manager MMC snap–in is used to configure Role–based permissions for applications. |
| certlm.msc | Certificate Manager for local computer | Certificate Manager (certlm.msc) MMC snap–in is used to manage the digital certificates stored in your local Windows Server. |
| certmgr.msc | Certificate Manager for current user | Certificate Manager (certmgr.msc) MMC snap–in is used to manage the digital certificates for the current user. |
| comexp.msc | Component Services Administration | Component Services MMC snap–in is used to manage Component Object Model (COM) and COM+ components. COM and COM+ allows software components to work together without knowing how those components work inside or in which language those components are written. COM+ is an enhanced version of COM. |
| compmgmt.msc | Local Computer Management | Computer Management MMC snap–in contains the System tools to manage the Local computer like Task Scheduler, Event Viewer, Shared Folders, Local Users and Groups, Computer Performance and Device manager. Computer Management MMC snap–in also has the tools to manage Local storage and Services. |
| devmgmt.msc | Device Manager | Device Manager MMC snap–in is used to manage the devices in your computer. Example – Uninstall Driver software, Update Driver software, Disable device etc. |
| diskmgmt.msc | Disk Management | Disk Management MMC snap–in is used to manage the local storage disks in your computer. |
| eventvwr.msc | Event Viewer | Event Viewer MMC snap–in is used to manage the Windows logs. Example – Application Events, Security Events, Setup Events and Forwarded Events. |
| fsmgmt.msc | Local Shared Folders | Local Shared Folders MMC snap–in displays shared folders, current open sessions, and current open files. |
| gpedit.msc | Local Computer Policy | Local Computer Policy MMC snap–in is used to edit and manage the local Group Policy Objects stored on a computer. Group Policy allows to manage configurations for computers and users through Group Policy settings. Example – Enforce password length and complexity requirements to maintain user account security. |
| lusrmgr.msc | Local Users and Groups | Local Users and Groups MMC snap–in is used to manages Local Users and Groups. Example – create a local user, delete a local user, add a local user to a local group etc. |
| perfmon.msc | Performance Monitor | Performance Monitor system monitoring MMC snap–in is used to monitor the whole system performance. Example – Processor performance, FileSystem Disk Activity, Server Work Queues, ReFS (Resilient File System), SMB Client Shares, SMB Server etc. |
| secpol.msc | Security Settings | Security Settings MMC snap–in is used to define security policies. |
| services.msc | Local Services | Local Services MMC snap–in is used to start, stop, and configure Windows Services. Windows Services are background processes running silently in the Operating System (usually without a user interface), similar to Daemons in Unix/Linux. |
| taskschd.msc | Task Scheduler | Task Scheduler MMC snap–in is used to schedule tasks to run automatically. |
| wbadmin.msc | Windows Server Backup | Windows Server Backup MMC snap–in is used to backup data to a local or remote location. |
| WF.msc | Windows Defender Firewall with advanced security | Windows Defender Firewall MMC snap–in is used to configure Windows Defender Firewall. |
| wlbadmin.msc | Local Backup | Local Backup MMC snap–in is used for local data backup or recovery. |
| WmiMgmt.msc | WMI Control | WMI Control MMC snap–in is used to configure and control Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) service. WMI provides management data to operating system and other apps. We can also automate administrative tasks using WMI scripts. |
Please visit the following link to learn how to add a snap-in file to MMC.
Different ways to open MMC
1 – Open MMC using PowerShell or Command Prompt
To open MMC (Microsoft Management Console), type "mmc.exe" from your Command Prompt or PowerShell terminal and press "Enter" button. Please refer below command.
PS C:\jajish>mmc.exe PS C:\jajish>
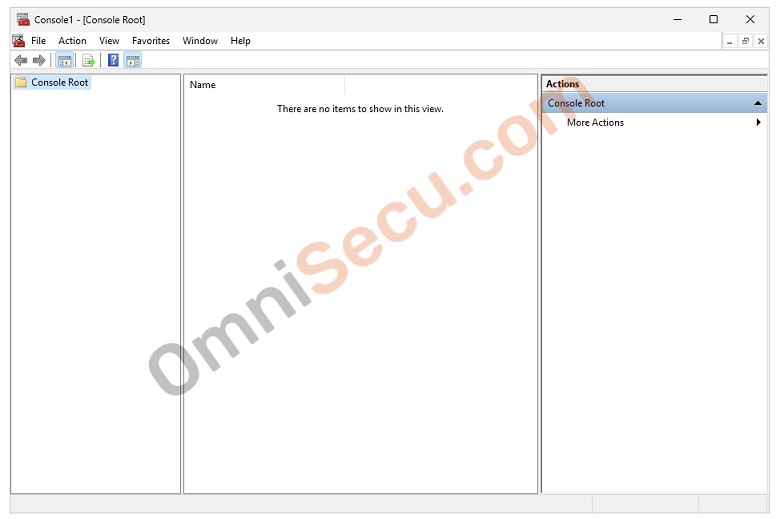
Following image shows the screenshot of a blank MMC Console, with no snap–in added.
2 – Open MMC using Windows Run dialog box
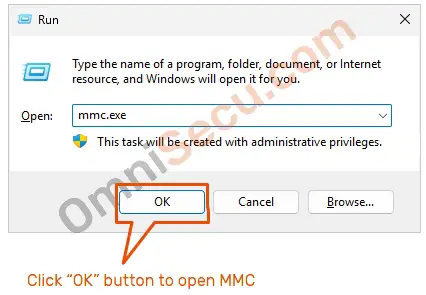
You can also open MMC (Microsoft Management Console), by typing mmc.exe in your Windows Run box, and then clicking "OK" button. Press Windows and R keys together to open the Windows Run box. Please refer below image.
3 – Open MMC using Windows Server search
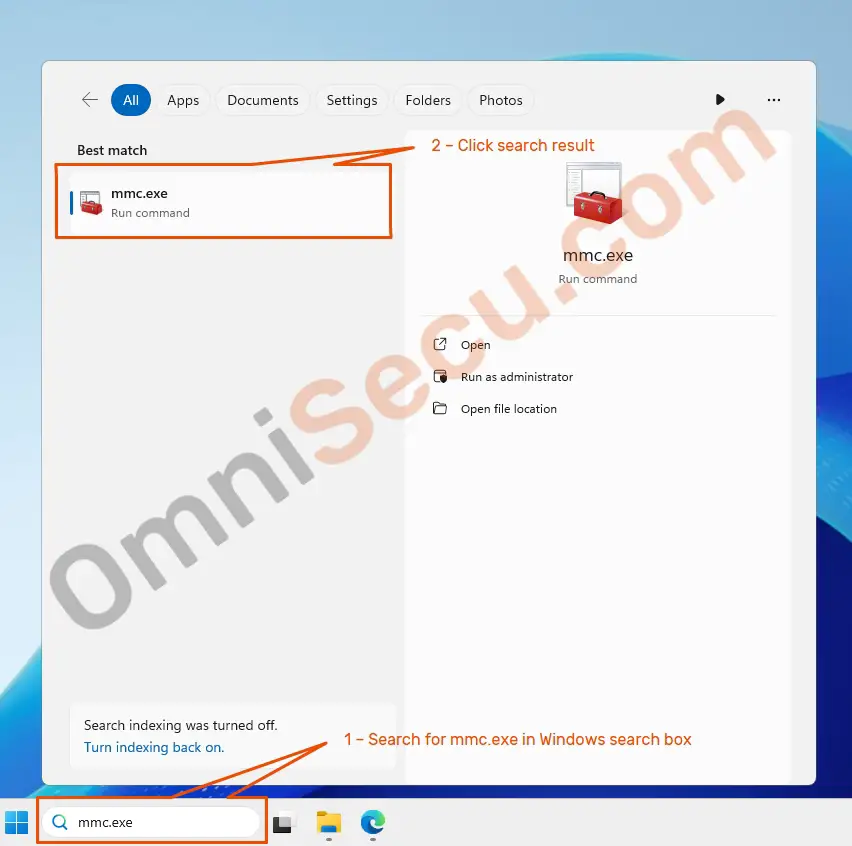
Search for mmc.exe inside Windows Server search box and then click the search result. Please refer below image.
Written by Jajish Thomas.
Last updated on 4th July, 2024.