How to configure IPv6 Address in Windows Server 2025 using PowerShell
IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) is the global organization responsible for managing DNS root, allocating IP addresses & AS numbers (Autonomous System Numbers) to five Regional Internet Registries, Protocol numbering system etc. IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) is run by ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers), another global organization.
Click the following link to learn more about the organizations which control the Internet, Network Protocols and Standards.
On Monday, January 31st, 2011, IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) allocated two pools of IPv4 to APNIC from the last remaining IPv4 addresses from the free pool. APNIC is the RIR (Regional Internet Registry) administering IP addresses for the Asia Pacific. Remaining IPv4 addresses from the free pools were allocated to the remaining RIRs (Regional Internet Registry) later. The world was in short of IPv4 addresses and IPv6 came later.
Please refer the following link to know more about the limitations of IPv4. IPv4 has already phased out from the computer networking industry. This tutorial lesson explains how to configure IPv6 Address in a computer running Windows Server 2025 Server Core, using PowerShell cmdlets.
If you are new to IPv6 or need to refresh your knowledge in IPv6, I suggest you to visit the following link to learn more about IPv6.
Step 1 - You must run PowerShell as the user "Administrator", to configure IPv6 address in Windows Server 2025. Make sure that you have logged-in as the user "Administrator" or you have logged-in as a user with administrative privileges to configure an IPv6 address. If the logged-in user id does not have administrative privileges, you can use "runas" command to run a PowerShell terminal as an administrator.
Please visit following link to learn how to run PowerShell as administrator in a Server Core computer.
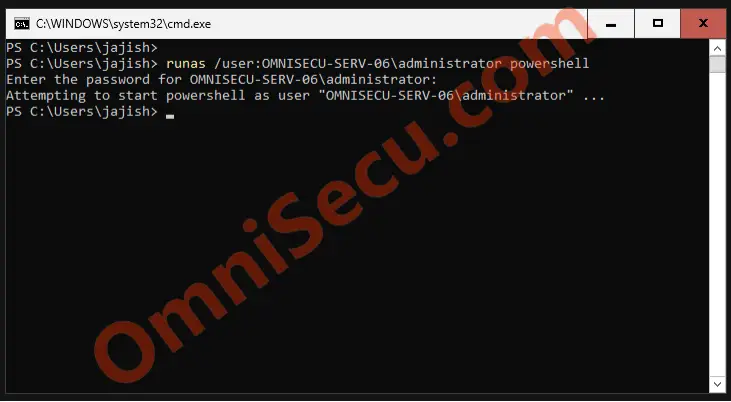
Step 2 – In a Windows Server 2025 Server Core installation, use "runas" command from cmd or PowerShell, to run PowerShell as administrator. Enter the password of administrator, when prompted. A PowerShell terminal window, with administrative privileges, will be opened once the "runas" command is run successfully.
C:\Users\jajish>runas /user:OMNISECU-SERV-06\administrator powershell Enter the password for OMNISECU-SERV-06\administrator: Attempting to start powershell as user "OMNISECU-SERV-06\administrator" ... C:\Users\jajish>
Please refer following screenshot.
Step 3 – Now, you need to identify the InterfaceIndex number of the network adapter, where you are going to configure IPv6 address, using PowerShell Cmdlets. Use "Get-NetAdapter" PowerShell cmdlet as shown below to get the InterfaceIndex number of the network adapter where you want to configure IPv4 address.
Get-NetAdapter | Format-List
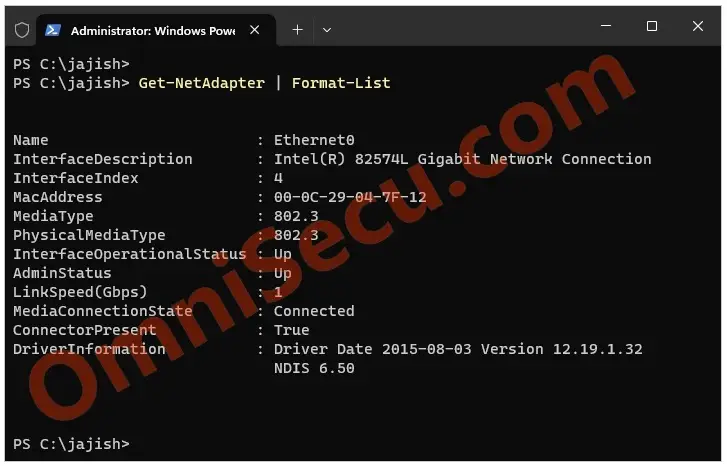
In this case, we have only one network interface in this computer. As you can see from the above output of Get-NetAdapter PowerShell cmdlet, the InterfaceIndex number is 3. We need to properly identify the network adapter and note it’s InterfaceIndex number. Every time when a PowerShell cmdlet related with this network adapter is run, we need to provide the InterfaceIndex number (in this case, the InterfaceIndex number is 3).
Step 4 - Once we had identified the network adapter and its InterfaceIndex number, we can use PowerShell "New-NetIPAddress" cmdlet to configure a new IPv6 address and Default Gateway address. You can see from the below "New-NetIPAddress" PowerShell cmdlet, you need to provide InterfaceIndex number when you run the cmdlet, to identify the network adapter.
From the below PowerShell cmdlet, you can understand that the IPv6 address we are configuring now is 2001:DB8:13FF::AAAA, Subnet prefix length is 64 (-PrefixLength 64) and IPv6 Default Gateway address we are configuring is 2001:DB8:13FF::1. Change the IPv6 address and other related settings as per your requirement.
Please note that the InterfaceIndex number used in the below "New-NetIPAddress" PowerShell cmdlet is 3. We found that number from "Get-NetAdapter" PowerShell cmdlet in Step 3.
New-NetIPAddress -IPAddress 2001:DB8:13FF::AAAA -InterfaceIndex 3 -DefaultGateway 2001:DB8:13FF::1 -AddressFamily IPv6 -PrefixLength 64
Written by Jajish Thomas.
Last updated on 4th July, 2024.