Differences between Server Core and GUI (Desktop Experience)
Similar to it’s previous version (Windows Server 2022), Windows Server 2025 can also be installed as a Server Core installation or Desktop Experience (with Graphical User Interface ‐ GUI) installation.
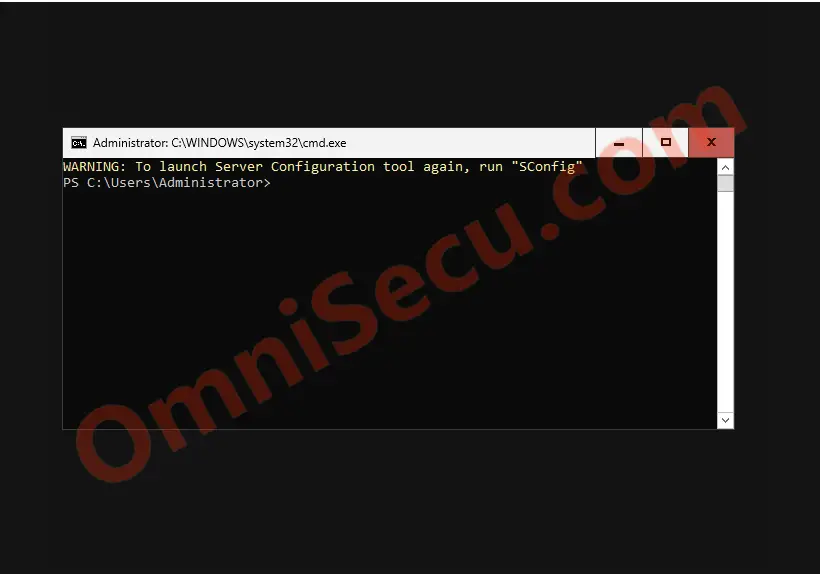
Below screenshot shows Windows Server 2025 installed as a Server Core installation. You can see that there is no GUI Desktop when you install Windows Server 2025 as a Server Core installation.
Windows Server 2025 Desktop Experience (Graphical User Interface – GUI) is the traditional Graphical User Interface for Microsoft Server Operating Systems. Windows Explorer and its Window style of apps for "computer user interaction" was used from the famous Network Operating System Windows NT, from early 1990s. Windows Explorer and its Graphical User Interface has evolved a considerable way from the Windows NT period.
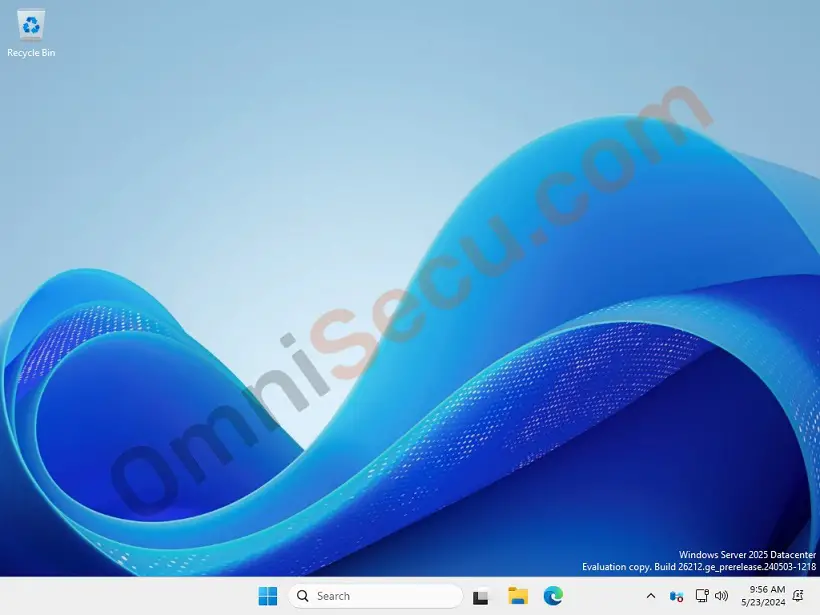
Below screenshot shows Windows Server 2025 installed as a Desktop Experience (with Graphical User Interface – GUI) installation. A Windows Server 2025 Desktop Experience installation has a Desktop similar to traditional Microsoft Windows Operating Systems.
As mentioned above, Windows Server 2025 Server Core installation does not have an in-built Graphical User Interface (GUI) like File Explorer and it’s Desktop. That means, you will not get the traditional Windows Desktop experience, when you install Windows Server 2022 as a Server Core installation. A computer with Server Core installation is meant to be managed remotely. A Server core installation can be managed locally using the command prompt (cmd.exe) or PowerShell terminal (powershell.exe). You can use Server Manager, Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) or Windows Admin Centre to manage Windows Server 2025 Server Core installation remotely.
The first obvious difference between Windows Server 2025 Desktop Experience installation and Server Core installation is that, Windows Server 2025 Desktop Experience installation has a Graphical User Interface. Windows Server 2025 with Desktop Experience installation is user friendly for all the computer users who are familiar with traditional Windows Graphical User Interface environment. Hence Windows Server 2025 Desktop Experience (with Graphical User Interface) is easier to manage locally or remotely for experienced or unexperienced system administrators.
Even though Windows Server 2025 Server Core installation does not have its main Desktop GUI environments, many GUI tools can available (by default) in Windows Server 2025 Server Core installation. Some of those default GUI tools are Task Manager (taskmgr.exe), Date & Time (control.exe timedate.cpl), Region (control.exe intl.cpl), System Information (msinfo32.exe), Windows installer (msiexec.exe), Notepad (notepad.exe), Registry Editor (regedit.exe or regedt32.exe). You can type the executable file names mentioned in bracket inside command prompt (cmd.exe) or PowerShell terminal (powershell.exe) to run those default GUI tools.
As the number of lines in the source code of any software increases, there are more chances for bugs and mistakes. Bugs and mistakes cause instability and security vulnerabilities. Server Core source code is much compact compared with Desktop Experience, because Desktop Experience needs many additional lines of code for Graphical User Interface (GUI) environment. Therefore, a Server Core installation is more stable and has less chances for security vulnerabilities.
A server computer is meant to serve you with some services like DNS, DHCP, Active Directory related services, File or Print server etc. The person who is in control and using those machines is not a layman, but a power user or a System Administrator. A graphical user interface (GUI) is not necessary for an experienced System Administrator to manage the Operating Systems. With a command prompt or PowerShell terminal an administrator can perform his duties.
A Desktop Experience (Graphical User Interface) installation will consume much more resources from the computer hardware than a Server Core installation. That resources may be Processor cycles, Memory or Disk usage. Those resources spent for GUI (Graphical User Interface) can be used as additional resources to the run the services on a Server Core installation.
Please visit the following Microsoft page, if you want to compare the differences between Server Core, or Server with Desktop experience.
Below table summarizes the main differences between Server Core and GUI.
| Component | Server Core | Desktop Experience (with GUI) |
|---|---|---|
| Graphical User interface | Minimal, command line driven (Command Prompt, PowerShell, SConfig) | All traditional Windows graphical user interface, including Windows Explorer |
| Disk space requirement | Small disk space only | More disks pace is required |
| RAM memory requirement | Less RAM requirement | More RAM is required |
| Manage Server Roles and features locally | Using PowerShell | Using GUI tools, Server Manager, PowerShell |
| Roles and Features | Some roles and features are not available | All roles and features are available |
| Remote management | Possible | Possible |
| Attack surface | No much attack surface | Comparatively more attack surface than Server Core |
| Stability | More stable | Comparatively less stable than Server Core |
| MMC (Microsoft Management Console) | Not installed by default – can be installed. | Installed |
Written by Jajish Thomas.
Last updated on 27th May, 2024.