How to run PowerShell as administrator
PowerShell is a scripting engine and a task automation program designed by Microsoft, mainly for Windows Operating Systems. PowerShell was first announced in November 14, 2006. PowerShell has a scripting language. PowerShell has also its own command–line terminal (similar to Command Prompt), named powershell.exe. It also has an Interactive Scripting Environment (ISE) named powershell_ise.exe.
The commands we use in PowerShell for administrative tasks are called as Cmdlets, which is pronounced as "command-lets".
Since PowerShell is used mainly for administrative tasks, you must run PowerShell as the superuser administrator. If you had logged-in to Windows Server as a user with no administrative privileges, please follow below steps to run PowerShell as an administrator
How to run PowerShell interactive command-line (powershell.exe) as administrator
Step 01 – Type powershell.exe in Windows search box as shown below.
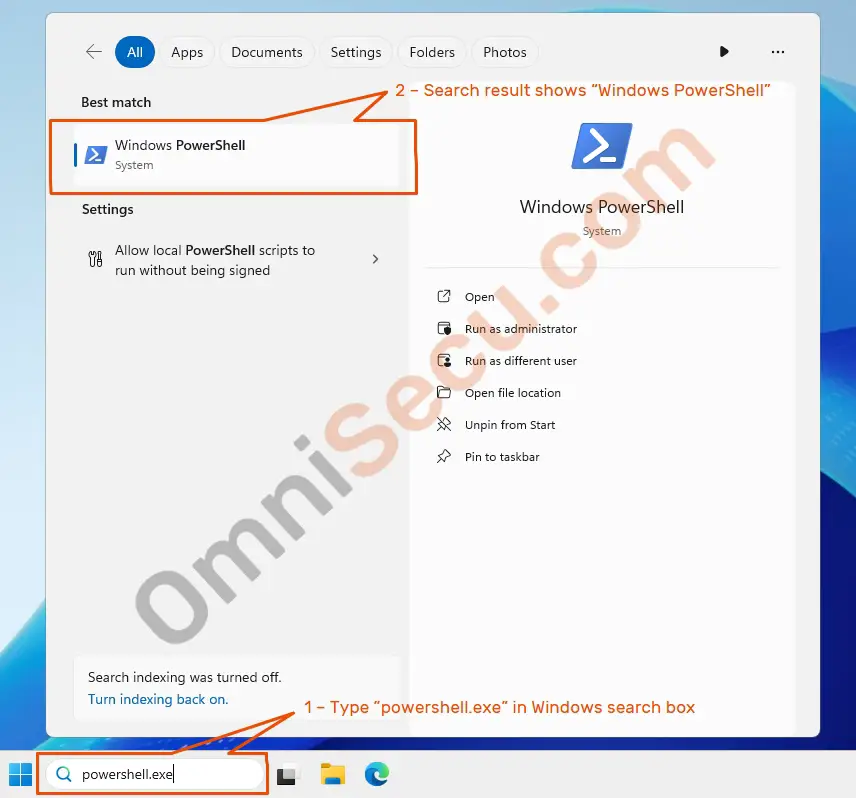
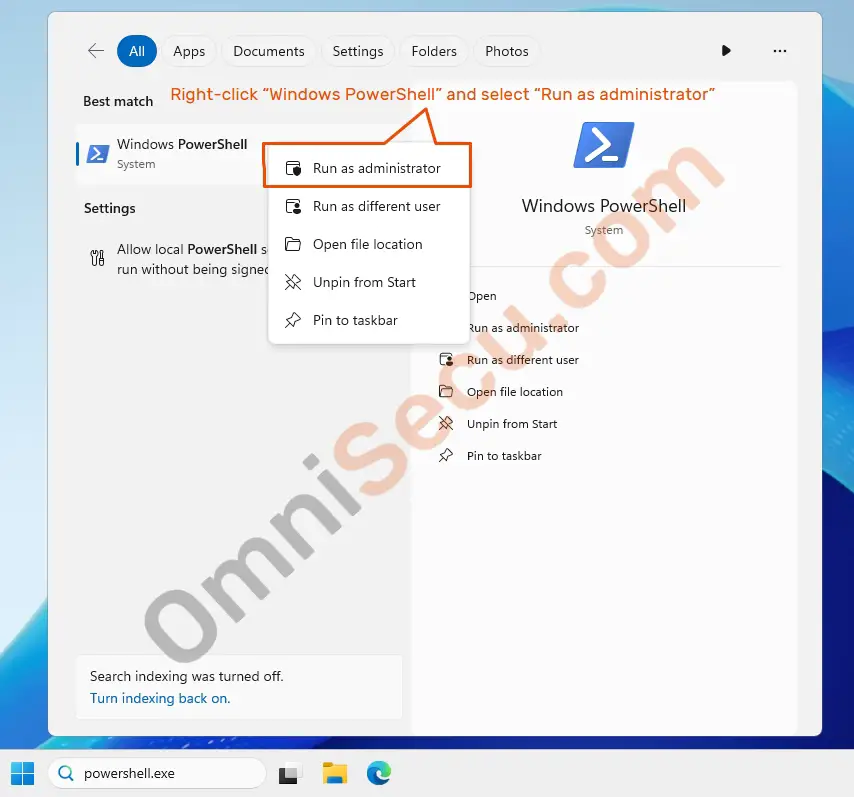
Step 02 – Right-click "Windows PowerShell" from the search results and select "Run as administrator" from the context menu, as shown in below screenshot.
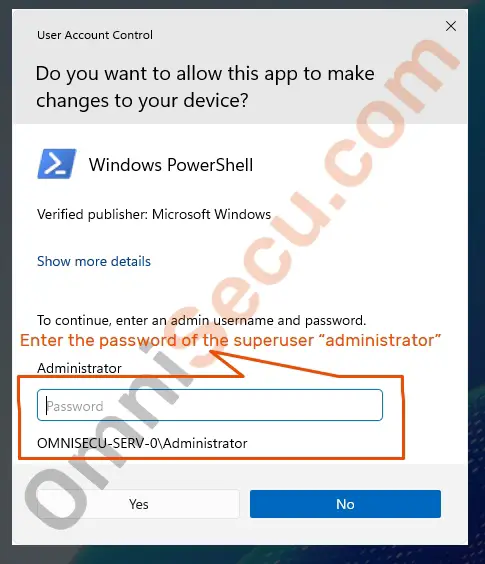
Enter the password of the user "administrator", and click "Yes" button.
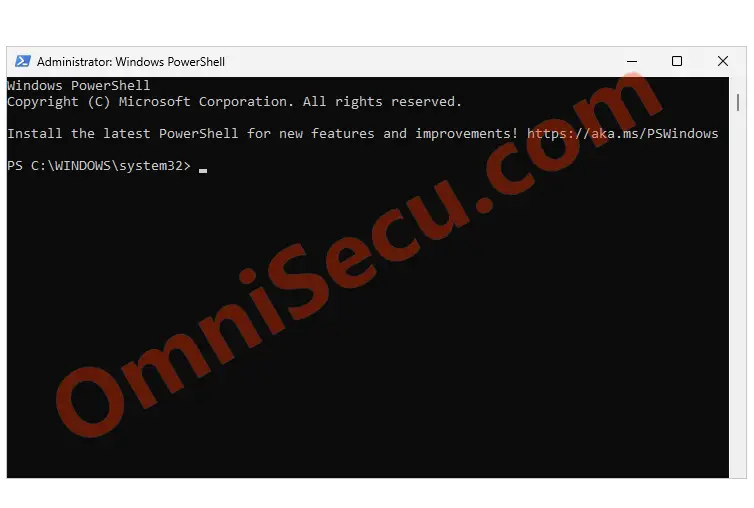
Windows PowerShell PowerShell interactive command-line (powershell.exe) terminal is now opened as administrator. You can run administrative commands as an administrator from this terminal.
How to run PowerShell ISE (Integrated Scripting Environment) as administrator
PowerShell ISE (Integrated Scripting Environment) is an tool for developing and debugging PowerShell scripts. PowerShell ISE is a very useful tool for developing and testing PowerShell scripts for Windows Operating System environments.
Step 01 – Type powershell_ise.exe in Windows search box as shown below.
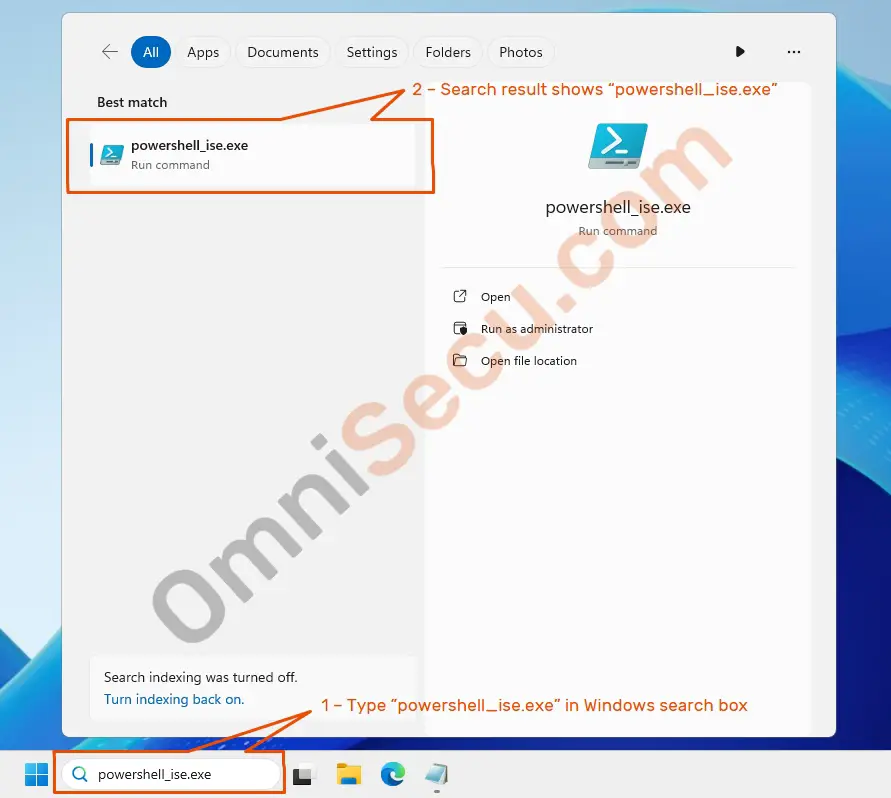
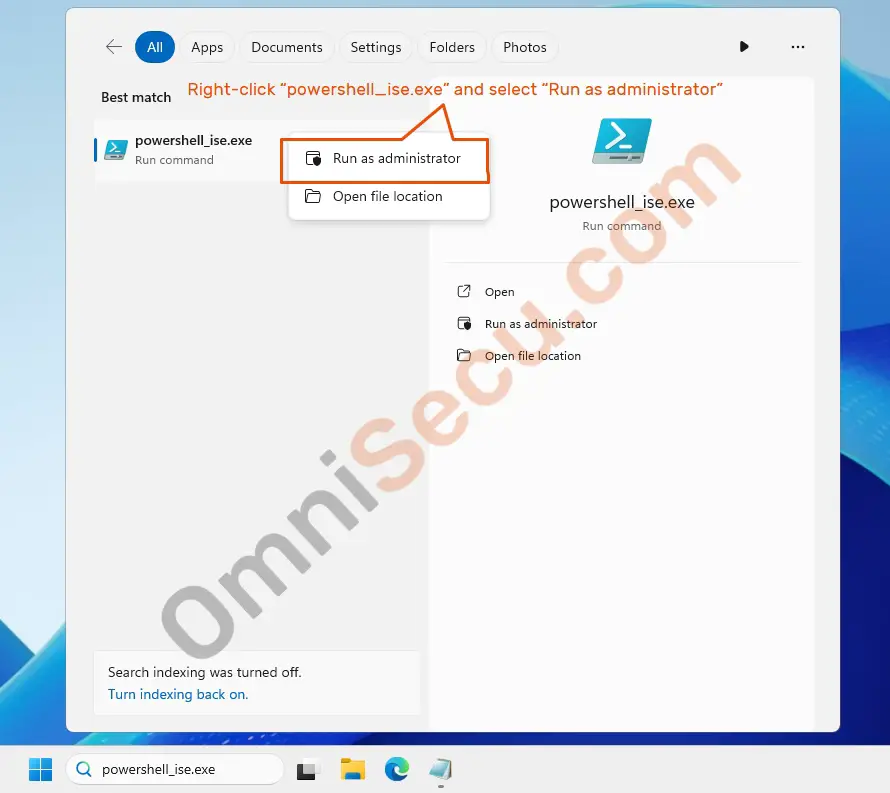
Step 02 – Right-click "powershell_ise.exe" from the search results and select "Run as administrator" from the context menu, as shown in below screenshot.
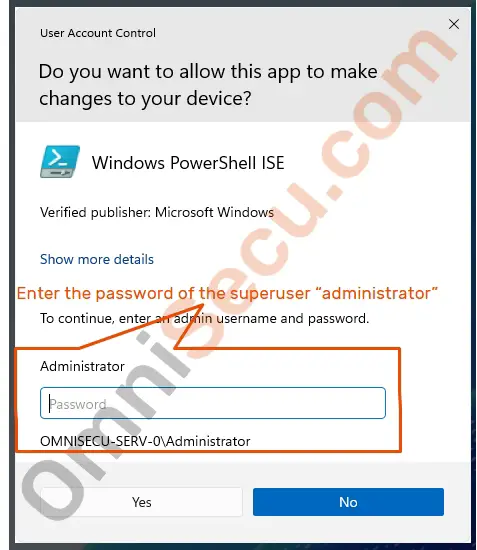
Enter the password of the user "administrator", and click "Yes" button.
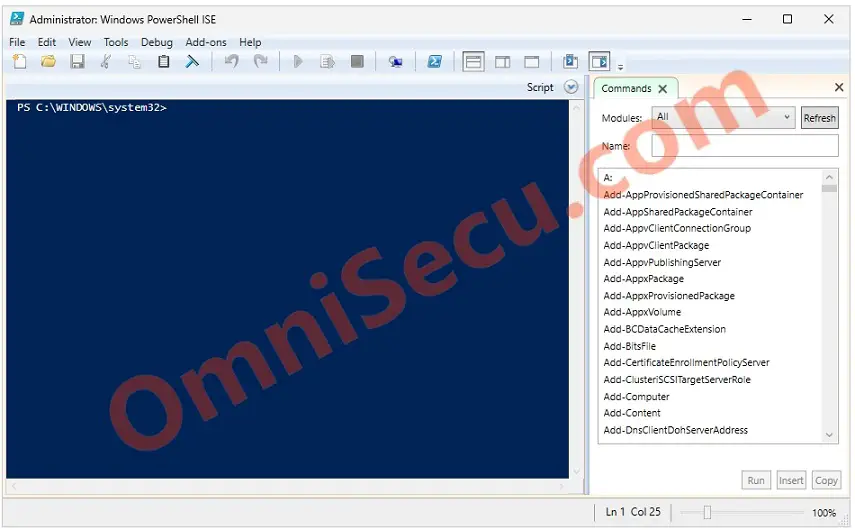
Windows PowerShell PowerShell interactive command-line (powershell.exe) terminal is now opened as administrator. You can run administrative commands as an administrator from this terminal.
Written by Jajish Thomas.
Last updated on 3rd June, 2024.