How to configure IPSec in Windows 2003 - Securing Telnet Traffic using IPSec
In this lesson and following lessons you will learn how to configure Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) in a Windows 2003 network and how to secure Telnet traffic using Internet Protocol Security (IPSec).
Telnet is a network protocol and is commonly used to refer to an application that uses that protocol. The application is used to connect to remote computers. Telnet listens at TCP well known port 23. Telnet is a terminal emulator software and is used to gain access to a command-line interface on a remote machine.
Securing Telnet Traffic using Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) - Scenario
You have four Windows 2003 servers, SERV03.omnisecu.com is a domain controller and SERV01.omnisecu.com, SERV02.omnisecu.com and SERV04.omnisecu.com are member servers.
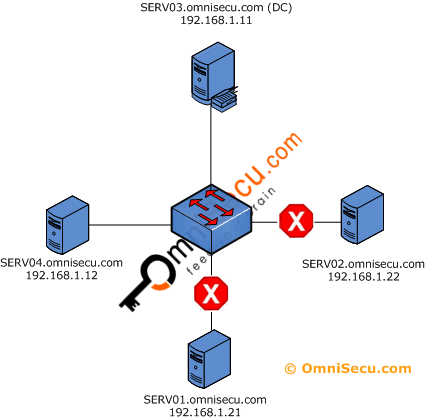
Figure 10: Scenario - Configure Internet Protocol Security in a Windows 2003 network.
You want to allow Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) secure Telnet traffic to your Windows 2003 domain controller SERV03.omnisecu.com from SERV04.omnisecu.com, which is a windows 2003 member server and to block Telnet access from all other servers to Windows 2003 domain controller SERV03.omnisecu.com.
You cannot use the default IPSec policies, because there is no default Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) policy to block Telnet traffic specifically.
Here we need to create a new Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) policy to permit secure Telnet access to the domain controller SERV03.omnisecu.com only from SERV04.omnisecu.com, and block Telnet traffic from all other servers.
In this lesson, you have learned an overview about telnet. You have four Windows 2003 servers. One is a Windows 2003 domain controller and other three are member servers. You want to allow only secure Telnet traffic to Windows 2003 domain controller from member server, SERV04.omnisecu.com. Click "Next" to continue.