What is localhost
The term "localhost" is used to refer the same local computer on which the TCP/IP protocol stack is running on. The term "localhost" is mapped internally to the loopback IP address 127.0.0.1 in most of the TCP/IP implementations.

Please visit following link to learn about IPv4 loopback addresses before continuing on this lesson.
When any program/protocol sends data from a computer with any IPv4 loopback address as the destination address, the TCP/IP protocol stack on that computer process the traffic within itself without sending it to the network.
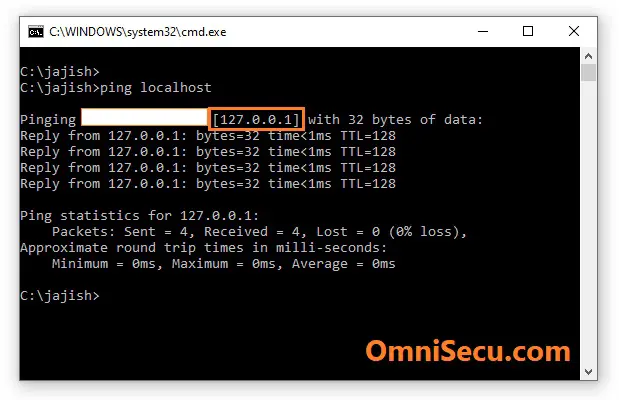
Refer below image, of a ping made to "localhost". You can see that the reply for ping command is coming back from loopback address , 127.0.0.1
When setting up a web server or any other type of server, you can use the term "localhost" to point to the same machine as the server. Since the term "localhost" maps to loopback address 127.0.0.1, you will get the response from the same local computer where the server is running.
I have a web server installed and running on this machine. See below image where I am using to get response from the same local computer, by using the term "localhost" (marked in browser’s address bar).

Related Tutorials
•
Introduction to TCP/IP, Features of TCP/IP, TCP/IP History, What is RFC (Request for Comments)
•
Seven Layers of OSI Model and functions of seven layers of OSI model
•
Five layered TCP/IP model
•
Network Layer (Layer 3)
•
TCP/IP Data Encapsulation and Decapsulation
•
Datalink Layer (Layer 2)
•
Ethernet Frame Format
•
What is MAC address or Layer 2 address or physical address
•
IPv4 Protocol, IPv4 header and fields of IPv4 header
•
IPv4 addresses, IPv4 Address Classes, IPv4 Address Classifications
•
What is Subnet Mask
•
What is network address
•
Limited broadcast address
•
Directed broadcast address
•
What is limited broadcast in IPv4 and how limited broadcast works
•
What is directed broadcast in IPv4 and how directed broadcast works
•
What is default gateway
•
What are private IP addresses - RFC 1918 private addresses
•
APIPA Addresses (Automatic Private IP Addresses)
•
What is loopback address in IPv4
•
What is localhost
•
Class A networks and Class A IP addresses
•
Class B networks and Class B IP addresses
•
Class C networks and Class C IP addresses
•
Class D multicast IP addresses
•
Subnetting - Part 1
•
Subnetting - Part 2
•
Subnetting - Part 3
•
Subnetting - Part 4
•
Subnetting - Part 5
•
Subnetting - Part 6
•
Variable Length Subnet Masking, VLSM, IP V4 Subnetting, subnetting tutorials, IP study guides, IP documentation, IP tutorials
•
Supernetting, IP Supernetting, IP Supernetting tutorial, How to Supernet, Supernetting Guide, Supernetting Concepts
•
How to find out the Network Address and Broadcast Address of a subnetted IPv4 address
•
Address Resolution Protocol Tutorial, How ARP work, ARP Message Format
•
What is Gratuitous ARP


