Ping command tool
Ping command (also called as Packet InterNet Groper) is a command line tool available in Cisco devices, Microsoft Windows, Unix and different flavors of GNU/Linux. Ping command tool is inbuilt and available out of the box in all Cisco/Windows/Unix/Linux Operating Systems. Ping command is one of the most used commandline tool for network troubleshooting. Ping command is used to test layer 3 network connectivity between two TCP/IP hosts. Ping command send a packet to the destination that we want to check is reachable, and if a reply is received back, we can make sure the destination is up, running and reachable.
I strongly recommend you to visit following lessons before reading further.
- Datalink Layer (Layer 2)
- Network Layer (Layer 3)
- IPv4 addresses, IPv4 Address Classes, IPv4 Address Classifications
- Internet Control Message Protocol, ICMP, How ICMP Work, ICMP Header, ICMP Message Header
- ICMP message types
- ICMP Echo Request and Echo Reply messages
How ping works
Ping command uses ICMP for checking the layer 3 network connectivity (in other words, checking network connectivity using IP addresses) between two TCP/IP devices. ICMP is an integral protocol of TCP/IP protocol stack. ICMP Echo request and Echo reply messages are used for testing layer 3 network connectivity between two computers.
The basic function of ping command tool is simple. Let us imagine that you want to test the layer 3 network connectivity to a remote computer, or you want to check whether a remote computer is up and running. You run ping commandline tool on your computer with the IPv4 address (layer 3 address) of the remote computer as the ping command parameter.

When you run the command, ping command generates and send one or more ICMP Echo request type of messages to the remote computer. When a TCP/IP computer receives an ICMP Echo request type of messages, it is obliged to reply with an ICMP Echo reply message back to the first computer.

If the remote computer is up and running and if that computer got the An ICMP Echo request type of message sent from the first computer, it will reply with an ICMP Echo reply type of message. If the first computer had received the ICMP Echo reply message from the remote computer, we can then make sure that there is no network connectivity issue and the remote computer is up and running.

An example of using ping command
Okay, let us see an example of using ping command. Open the command prompt program in your Windows computer by typing cmd in search box, and then by clicking the command prompt from search result.
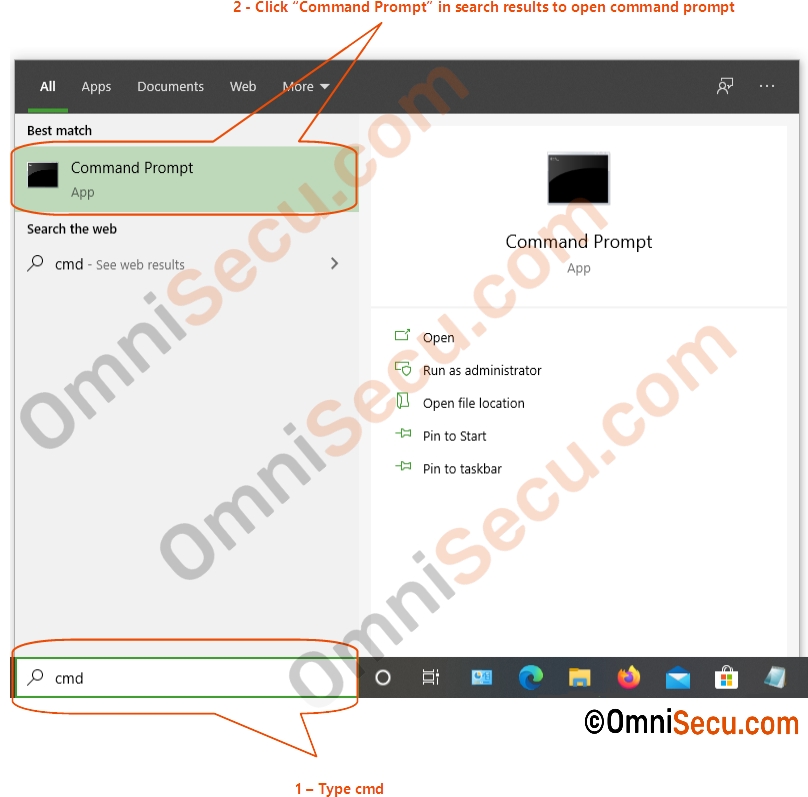
Type ping with the IPv4 address of the remote computer and hit Enter key. In this example, I had entered the IPv4 address 1.1.1.1 as the parameter of ping command. 1.1.1.1 is the IPv4 address of a free DNS (Domain Name System) server owned by Cloudflare. I need to check whether I have connectivity to DNS server 1.1.1.1.
You may also use ping command with a domain name. The ping command then resolve the domain name into an IPv4 address and starts sending ICMP Echo request type of message to the destination IPv4 address.

Ping command output shows it had sent 4 ICMP Echo request type of messages from my computer to the remote computer and got ICMP Echo reply messages for all those four ICMP Echo request messages. Packet loss is 0%.
If there is a network connectivity issue and the remote computer is unreachable, you will get the ping command output similar to below screenshot.
