ICMP Echo Request and Echo Reply messages
ICMP Echo Request and ICMP Echo Reply messages are used for network connectivity testing and troubleshooting purposes. If a person at a computer wants to test the Layer 3 network connectivity to another computer (located locally or remotely), he can use network troubleshooting tools like Ping, Traceroute/Tracert, Pathping etc., to generate and send ICMP Echo Request messages to other computer. When the other computer he was trying to troubleshoot the connectivity receives the ICMP Echo Request message, it will send back an ICMP Echo Reply message to the first computer.
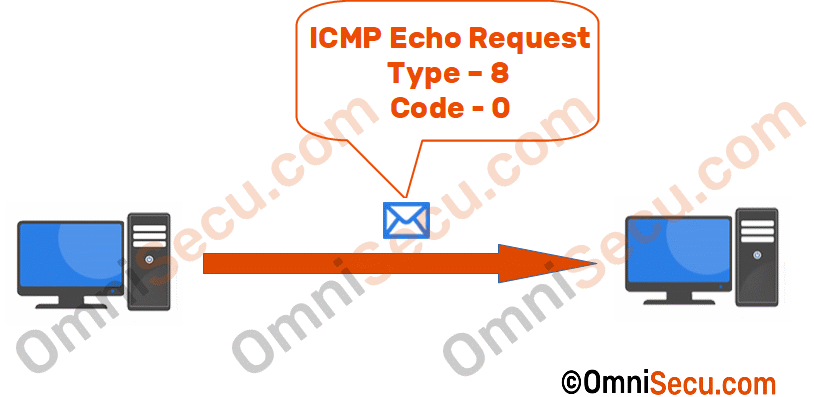
Once the ICMP Echo Reply is received from the other computer we can make sure that Layer 3 connectivity exists between those two computers/hosts.
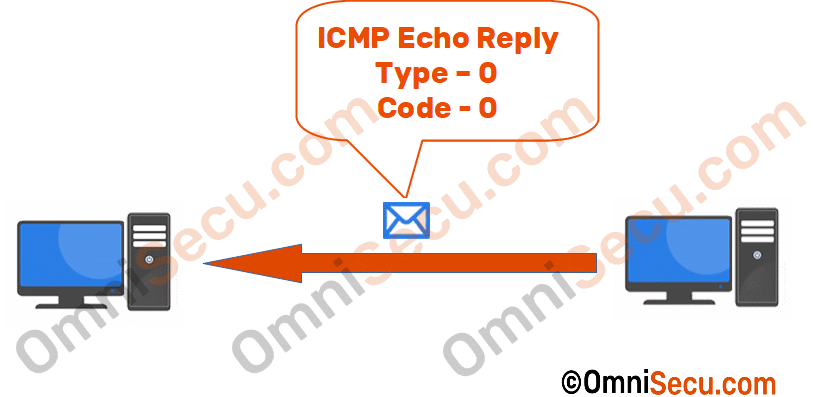
Format of ICMP Echo Request message and Echo Reply message is shown in below image.
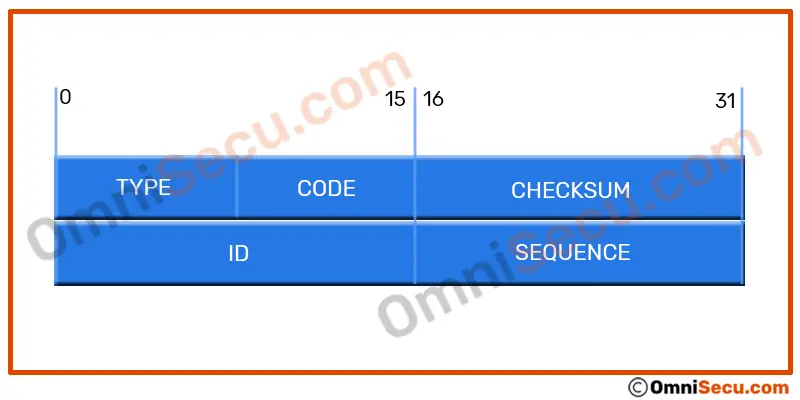
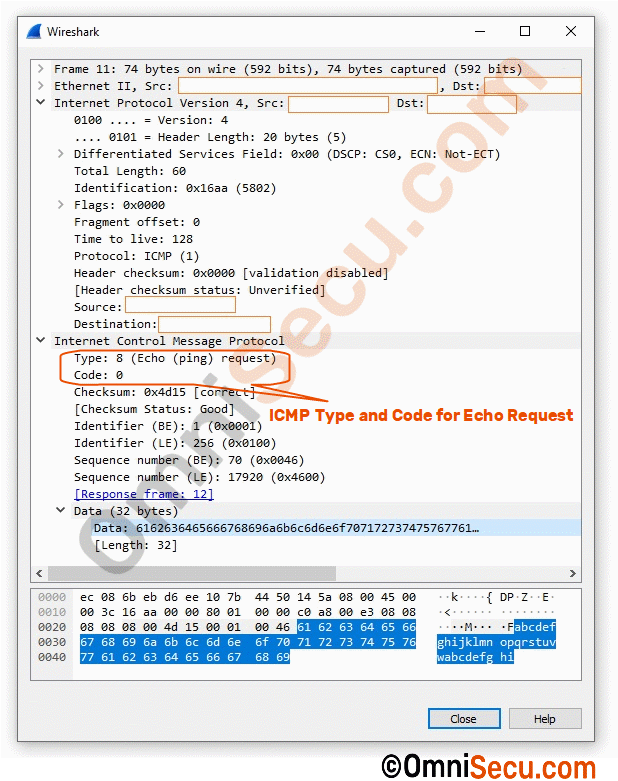
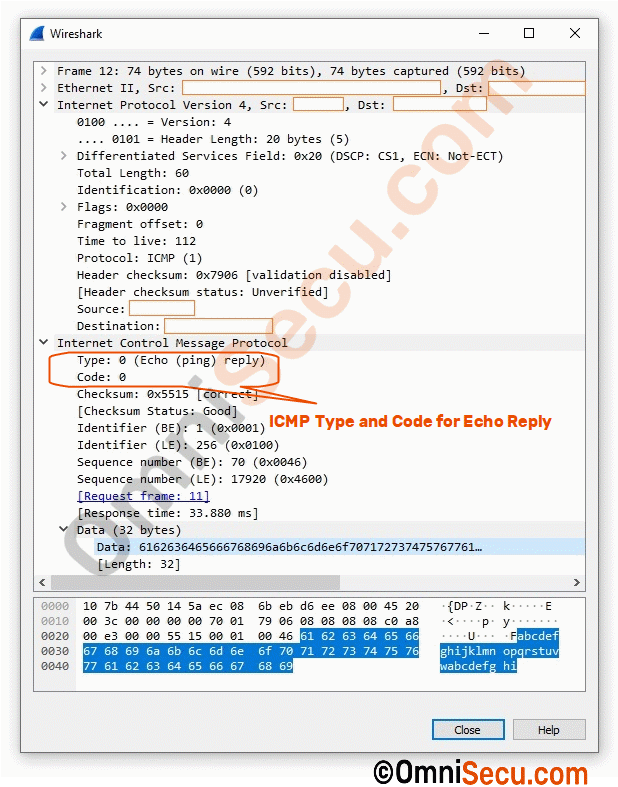
As discussed in the ICMPv4 header lesson, ICMP Echo Request message has its Type as 8 and Code as 0. ICMP Echo Reply message has its Type as 0 and Code as 0. Note that the Code field in ICMP header has is same value for (0) ICMP Echo Request message and ICMP Echo Reply message. Please click next link to know more about Type and Code fields in ICMP header
The ID (Identifier) and the Sequence fields in ICMP Echo Request and Echo Reply messages are used to match a particular Echo Request with its corresponding Echo Reply.
Data payload of ICMP Echo Request packet is used for padding, using ASCII characters. ICMP Echo Reply packet must have the same data payload as the ICMP Echo request.
Screenshot of Wireshark packet capture of an ICMP Echo Request message is coiped below.
Screenshot of Wireshark packet capture of an ICMP Echo Reply message is coiped below.
Related Tutorials
•
Introduction to TCP/IP, Features of TCP/IP, TCP/IP History, What is RFC (Request for Comments)
•
Seven Layers of OSI Model and functions of seven layers of OSI model
•
Five layered TCP/IP model
•
Network Layer (Layer 3)
•
TCP/IP Data Encapsulation and Decapsulation
•
Datalink Layer (Layer 2)
•
Ethernet Frame Format
•
What is MAC address or Layer 2 address or physical address
•
IPv4 Protocol, IPv4 header and fields of IPv4 header
•
IPv4 addresses, IPv4 Address Classes, IPv4 Address Classifications
•
What is Subnet Mask
•
What is network address
•
Limited broadcast address
•
Directed broadcast address
•
What is limited broadcast in IPv4 and how limited broadcast works
•
What is directed broadcast in IPv4 and how directed broadcast works
•
What is default gateway
•
What are private IP addresses - RFC 1918 private addresses
•
APIPA Addresses (Automatic Private IP Addresses)
•
What is loopback address in IPv4
•
What is localhost
•
Class A networks and Class A IP addresses
•
Class B networks and Class B IP addresses
•
Class C networks and Class C IP addresses
•
Class D multicast IP addresses
•
Subnetting - Part 1
•
Subnetting - Part 2
•
Subnetting - Part 3
•
Subnetting - Part 4
•
Subnetting - Part 5
•
Subnetting - Part 6
•
Variable Length Subnet Masking, VLSM, IP V4 Subnetting, subnetting tutorials, IP study guides, IP documentation, IP tutorials
•
Supernetting, IP Supernetting, IP Supernetting tutorial, How to Supernet, Supernetting Guide, Supernetting Concepts
•
How to find out the Network Address and Broadcast Address of a subnetted IPv4 address
•
Address Resolution Protocol Tutorial, How ARP work, ARP Message Format
•
Internet Control Message Protocol, ICMP, How ICMP Work, ICMP Header, ICMP Message Header
•
ICMP message types
•
ICMP Destination Unreachable messages
•
ICMP Source Quench messages
•
ICMP Redirect messages
•
ICMP Router Advertisement messages
•
ICMP Router Solicitation messages
•
ICMP Time Exceeded messages
•
ICMP Parameter Problem messages
•
ICMP Timestamp Request and Timestamp Reply messages
•
ICMP Photuris messages




