Authentication Header, AH, Internet Protocol Security IPSec
The Authentication Header (AH) is an IPSec protocol that provides data integrity, data origin authentication, and optional anti-replay services to IP. Authentication Header (AH) does not provide any data confidentiality (Data encryption). Since Authentication Header (AH) does not provide confidentiality, there is no need for an encryption algorithm. AH protocol is specified in RFC 2402.
Authentication Header (AH) is an IP protocol and has been assigned the protocol number 51 by IANA. In the IP header of Authentication Header (AH) protected datagram, the 8-bit protocol field will be 51, indicating that following the IP header is an Authentication Header (AH) header.
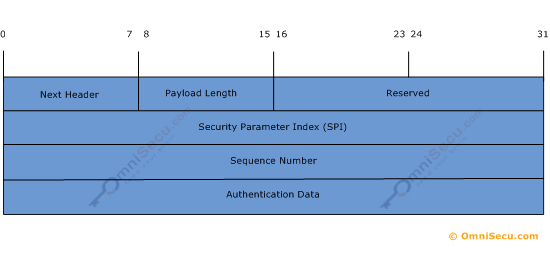
Figure 6: Authentication Header (AH) - Header
Next Header: Next header field points to next protocol header that follows the AH header. It can be a Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) header, a TCP header or a UDP header (depending on the network application).
Payload Length: specifies the length of AH in 32-bit words (4-byte units), minus 2.
RESERVED: This field is currently set to 0, reserved for future use.
Security Parameter Index (SPI): The Security Parameter Index (SPI) field contains the Security Parameter Index, is used to identify the security association used to authenticate this packet.
Sequence Number: Sequence Number field is the number of messages sent from the sender to the receiver using the current SA. The initial value of the counter is 1. The function of this field is to enable replay protection, if required.
Authentication Data: The Authentication Data field contains the result of the Integrity Check Value calculation, that can be used by the receiver to check the authentication and integrity of the packet. This field is padded to make total length of the AH is an exact number of 32-bit words. RFC 2402 requires that all AH implementations support at least HMAC-MD5-96 and HMAC-SHA1-96.