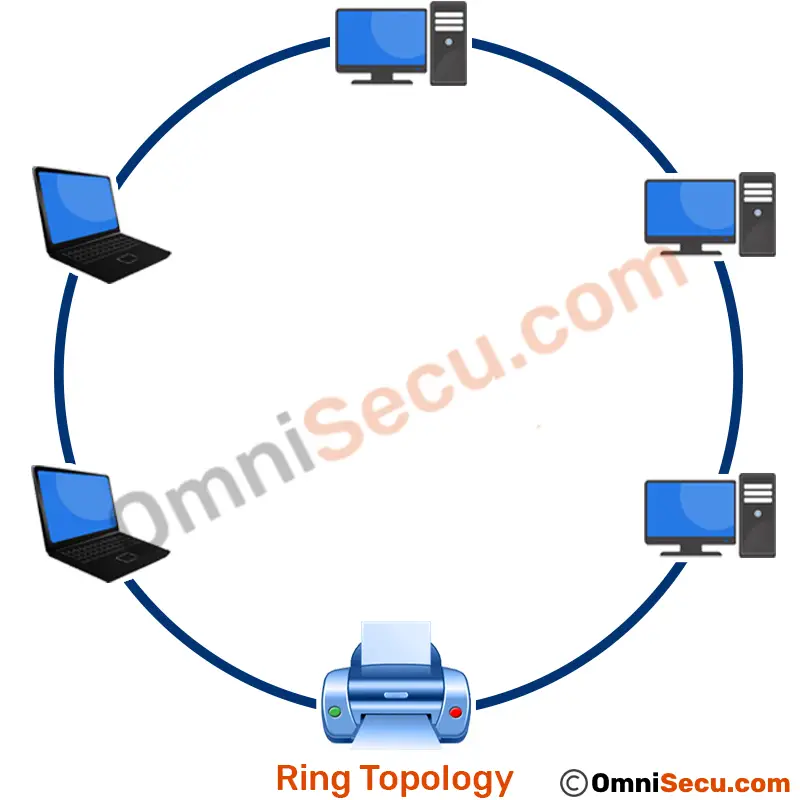
Ring Topology in networking
In a ring topology, all devices in the network are connected via a cable that loops in a logical ring or circle. In ring topology, the data circulates in a logical ring shape within the network.
The physical shape of the network need not be in ring or circular shape. A ring topology can be a logical circle that has no start and no end. Terminators are not necessary in a ring topology. Signals travel in one direction on a ring while they pass from one computer to the next. Each device in ring topology can regenerate the data signal, so that the data signal may travel the required distance, without signal quality deterioration.
Logical ring networks are wired like star topology. For example; in a Token Ring network, a Multistation Access Unit (MAU) plays the role of a network switch on an Ethernet star topology based network. The physical layout of ring topology looks similar to star topology.
Below image shows a Multistation Access Unit (MAU).

The main advantage of ring topology is that the signal degeneration is low since each workstation participating in the network is responsible for regenerating the weak signal.
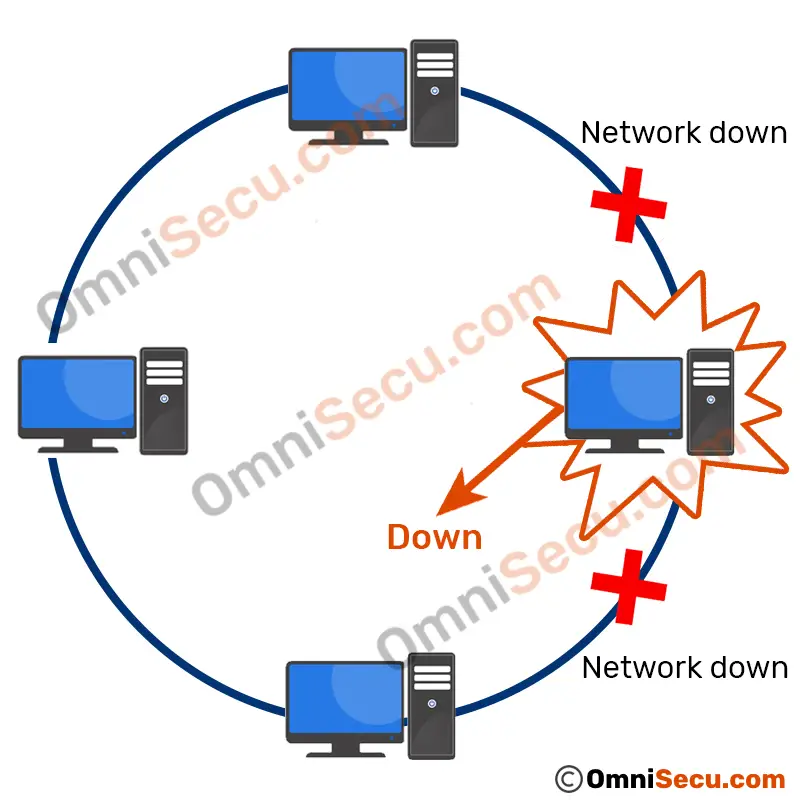
The disadvantage of ring topology is that the failure of one device in the network can cause the failure entire network. Ring down can happen also when computers are added or removed from the network. Ring will become down also when any network maintenance happen.