How BPDU is generated and How BPDU works
There are two types of Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) and they are Configuration BPDUs and Topology Change Notification (TCN) BPDUs.
In a layer 2 Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) enabled network, Configuration BPDUs are generated from the Root Bridge (Root Switch) and flow outward along the active Paths and move away from the Root Bridge (Root Switch).
Topology Change Notification BPDUs (TCN BPDUs) are generated normally from Non-Root Switchs and flow upstream towards the Root Bridge (Root Switch) to inform the Root Bridge (Root Switch) that the network topology has changed.
Click the following link to learn more about Topology changes in Spanning Tree Protocol (STP).
Following network topology image shows how Configuration BPDUs are generated from the Root Bridge (Root Switch) and flow outward along the active Paths and move away from the Root Bridge (Root Switch).
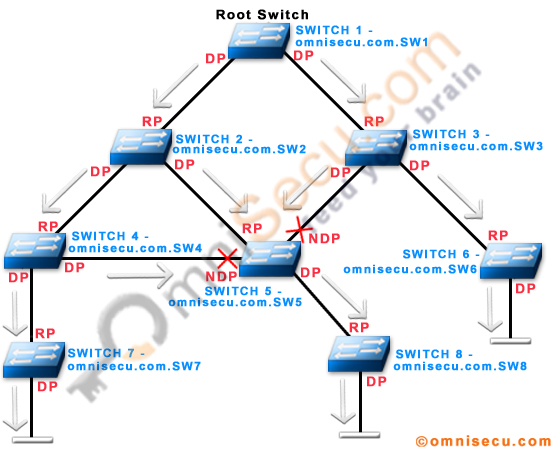
A Switch with lowest Switch ID is selected as the Root Bridge (Root Switch) . When a Network Switch receives a configuration BPDU that has a lower Root Switch (Root Bridge) ID, compared with what the Network Switch has as lower Root Switch (Root Bridge) ID, the Network Switch will consider the Switch with lowest Root Switch (Root Bridge) ID as the Root Bridge (Root Switch) and start relaying the Configuration BPDUs which are received from the new Root Bridge (Root Switch) .
After the Root Bridge (Root Switch) has been identified, all other Non-Root Switches bridges do not actually generate Configuration BPDUs. Non-Root Switch only propagates the BPDUs generated by the Root Bridge (Root Switch) . The Non-Root Switch also updates certain fields in the Configuration BPDUs, such as Message Age, Root Path Cost, Sender Bridge ID etc.
When a port receives a BPDU, it has a path to the Root Bridge (Root Switch), because BPDUs are originated from the Root Bridge (Root Switch). The port which receives a BPDU is normally a Root Port. For a Non-Root Bridge a port that receives a BPDU, that port leads to the Root Bridge (Root Switch).
If a Non-Root Bridge receives BPDUs in two ports, probably the network is in a Layer 2 loop.